Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 73, 2015/03
Using a collimating heavy-ion microbeam system, we have explored various effects of heavy-ion hit on biological materials. However, there are limitations of the collimating system in the size of the microbeam spot and in the irradiation speed that cannot be overcome in principle. Thus, we started the development of a focusing microbeam system for target-irradiating individual cells more precisely. In this year, we established the protocol for irradiating "actual" cell sample with scanned beam. In the experiment, the HeLa cells were inoculated on a CR-39 film, then place on the sample stage. The microscopic image of cells was analyzed, and the cells were irradiated with scanned neon microbeam. After irradiation, we found the correspondence of the distribution pattern of the ion hit positions and the  -H2AX foci on cell nuclei, indicating rapid and accurate irradiation of individual cells with the focusing heavy-ion microbeam.
-H2AX foci on cell nuclei, indicating rapid and accurate irradiation of individual cells with the focusing heavy-ion microbeam.
Matsumoto, Hideki*; Tomita, Masanori*; Otsuka, Kensuke*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Maeda, Munetoshi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Ikeda, Hiroko; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 76, 2015/03
The objective of this project is to elucidate molecular mechanisms for the induction of radioadaptive response through radiation-induced bystander responses induced by irradiation with heavy ion microbeams in JAEA. We found that the adaptive response was induced by Ar (520 MeV  Ar
Ar ) microbeam-irradiation of a limited number of cells, followed by the broad beam-irradiation and that the adaptive response was almost completely suppressed by the addition of carboxy-PTIO, as a nitric oxide (NO) scavenger. In addition, we found several genes induced specifically and preferentially when radioadaptive response could be induced. We confirmed that
) microbeam-irradiation of a limited number of cells, followed by the broad beam-irradiation and that the adaptive response was almost completely suppressed by the addition of carboxy-PTIO, as a nitric oxide (NO) scavenger. In addition, we found several genes induced specifically and preferentially when radioadaptive response could be induced. We confirmed that 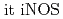 expression was specifically induced only when radioadaptive response could be induced. Our findings strongly suggested that radioadaptive response can be induced by NO-mediated bystander responses evoked by irradiation with heavy ion microbeams.
expression was specifically induced only when radioadaptive response could be induced. Our findings strongly suggested that radioadaptive response can be induced by NO-mediated bystander responses evoked by irradiation with heavy ion microbeams.
Tomita, Masanori*; Matsumoto, Hideki*; Otsuka, Kensuke*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 77, 2015/03
Radiation-induced bystander responses are defined as responses in cells that have not been directly targeted by radiation but are in the neighborhood of cells that have been directly exposed. In this study, we aim to clarify a role of bystander response to sustain the homeostasis of damaged tissue using heavy-ion microbeams. We established the heavy-ion microbeam irradiation method to a 3D cultured human epidermis. Using this method, a viable cell rate of the 3D cultured human epidermis irradiated with 260 MeV  Ne-ion microbeams or broadbeams was analyzed by the MTT method.
Ne-ion microbeams or broadbeams was analyzed by the MTT method.
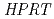 locus in normal human fibroblasts induced by C-, Ne- and Ar-ion microbeams
locus in normal human fibroblasts induced by C-, Ne- and Ar-ion microbeamsSuzuki, Masao*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Muto, Yasuko*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Ikeda, Hiroko; Hattori, Yuya; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 78, 2015/03
We have been studying the radiation-quality dependent bystander cellular effects, such as cell killing, mutation induction and chromosomal damage, using heavy-ion microbeams with different ion species. This year we focused on the ion-species dependent bystander mutagenic effect on 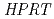 locus in normal human fibroblasts. The confluent culture were irradiated using a 256 (16
locus in normal human fibroblasts. The confluent culture were irradiated using a 256 (16 16)-cross-stripe method using C, Ne and Ar microbeam. Gene mutation on
16)-cross-stripe method using C, Ne and Ar microbeam. Gene mutation on 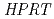 locus was detected with 6-thioguanine resistant clones. The mutation frequency in cells irradiated with C-ion microbeams was 6 times higher than that of non-irradiated control cells and of the sample treated with specific inhibitor of gap-junction cell-to-cell communication. On the other hand, no enhanced mutation frequencies were observed in cells irradiated with either Ne- or Ar-ion microbeams. There is clear evidence that the bystander mutagenic effect via gap-junction communication depends on radiation quality.
locus was detected with 6-thioguanine resistant clones. The mutation frequency in cells irradiated with C-ion microbeams was 6 times higher than that of non-irradiated control cells and of the sample treated with specific inhibitor of gap-junction cell-to-cell communication. On the other hand, no enhanced mutation frequencies were observed in cells irradiated with either Ne- or Ar-ion microbeams. There is clear evidence that the bystander mutagenic effect via gap-junction communication depends on radiation quality.
Yasuda, Takako*; Oda, Shoji*; Asaka, Tomomi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Muto, Yasuko*; Ikeda, Hiroko; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Mitani, Hiroshi*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 85, 2015/03
In this present study, we examined the effects of heavy carbon-ions on development in pre-implantation period utilizing medaka blastula stage embryos (st. 11: blastderm diameter is about 500  m). We performed targeted irradiation by carbon-ion micro-beam (diameters of 120, 180
m). We performed targeted irradiation by carbon-ion micro-beam (diameters of 120, 180  m) to a central parts of blastoderm and observed the abnormalities during development compared with whole-body irradiated embryos. As a results, retardation and characteristic malformed eyes were observed during development when blastoderm cells were partially irradiated, However, more than half of 50 Gy-irradiated embryos (area size=120
m) to a central parts of blastoderm and observed the abnormalities during development compared with whole-body irradiated embryos. As a results, retardation and characteristic malformed eyes were observed during development when blastoderm cells were partially irradiated, However, more than half of 50 Gy-irradiated embryos (area size=120  m diameter) could hatch normally in contrast to all embryos with 2 Gy of whole-body irradiation being lethal before hutching.
m diameter) could hatch normally in contrast to all embryos with 2 Gy of whole-body irradiation being lethal before hutching.
Autsavapromporn, N.*; Plante, I.*; Liu, C.*; Konishi, Teruaki*; Usami, Noriko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Azzam, E.*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Suzuki, Masao*
International Journal of Radiation Biology, 91(1), p.62 - 70, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:93.49(Biology)Radiation-induced bystander effects have important implications in radiotherapy. Their persistence in normal cells may contribute to risk of health hazards, including cancer. This study investigates the role of radiation quality and gap junction intercellular communication (GJIC) in the propagation of harmful effects in progeny of bystander cells. Confluent human skin fibroblasts were exposed to microbeam radiations with different linear energy transfer (LET) by which 0.036 0.4% of the cells were directly targeted by radiation. Following 20 population doublings, the cells were harvested and assayed for micronucleus formation, gene mutation and protein oxidation. The results showed that expression of stressful effects in the progeny of bystander cells is dependent on LET.
0.4% of the cells were directly targeted by radiation. Following 20 population doublings, the cells were harvested and assayed for micronucleus formation, gene mutation and protein oxidation. The results showed that expression of stressful effects in the progeny of bystander cells is dependent on LET.
Oshima, Takeshi; Sato, Takahiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Onoda, Shinobu; Hirao, Toshio; Ito, Hisayoshi
Materials Science Forum, 527-529, p.1347 - 1350, 2006/00
Charge induced in 6H-SiC pn diodes by oxygen ion microbeams was examined in an energy range between 6 and 18 MeV. To minimize the influence of damage, single ion hit Transient Ion Beam Induced Current (TIBIC) measurement system, in which the transient current induced by single ion incidence can be measured, was used in this study. The value of charge increases with increasing reverse applied bias, and the saturation of charge is observed when the depletion layer becomes longer than ion range. An increase of collected charge by the funneling effect (the generation of a transient electric filed) is observed in the case of the depletion layer shorter than ion range. The charge collection efficiency is estimated to be 100 % in the saturation region (the depletion layer longer than ion range). It strongly suggests that high quality particle detectors are fabricated using SiC.
Yamakawa, Takeshi; Hirao, Toshio; Abe, Hiroshi; Onoda, Shinobu; Wakasa, Takeshi; Shibata, Toshihiko*; Kamiya, Tomihiro
JAERI-Review 2004-025, TIARA Annual Report 2003, p.19 - 20, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
Oshima, Takeshi; Sato, Takahiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Yamakawa, Takeshi; Onoda, Shinobu; Wakasa, Takeshi; Laird, J. S.; Hirao, Toshio; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Ito, Hisayoshi; et al.
Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Application (RASEDA-6), p.177 - 180, 2004/10
no abstracts in English
Lee, K. K.; Oshima, Takeshi; Saint, A.*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Jamieson, D. N.*; Ito, Hisayoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.489 - 494, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:78.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)To obtain the information on radiation damage of 6H-SiC devices, ion beam induced charge collection (IBICC) for 6H-SiC schottky diodes irradiated with proton, alpha and carbon micro beam 10 to 10
to 10 ions/cm
ions/cm was studied. No significant difference of degradation was observed between p- and n-substrates irradiated with 2MeV-alpha micro beam. The decrease in IBCC shows a good agreement with the calculation using non ionizing energy loss (NIEL). As a result of ion luminescence and ultra violet photo luminescence, the level of 2.32 eV was observed.
was studied. No significant difference of degradation was observed between p- and n-substrates irradiated with 2MeV-alpha micro beam. The decrease in IBCC shows a good agreement with the calculation using non ionizing energy loss (NIEL). As a result of ion luminescence and ultra violet photo luminescence, the level of 2.32 eV was observed.
Kamiya, Tomihiro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Oshima, Takeshi; Hirao, Toshio; Lee, K. K.; Onoda, Shinobu*; Laird, J. S.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 210, p.206 - 210, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Souno, T.*; Hattori, M.*; Nishihara, Y.*; Oki, Y.*; Watanabe, E.*; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Arakawa, Kazuo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 191(1-4), p.342 - 345, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.4(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Tomihiro
Radioisotopes, 50(8), p.42 - 48, 2001/08
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sakai, Takuro; Hirao, Toshio; Oikawa, Masakazu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 181(1-4), p.280 - 285, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.1(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 , by localized irradiation of heavy ion microbeams
, by localized irradiation of heavy ion microbeamsKiguchi, Kenji*; Kinjo, Y.*; Masahashi, K.*; Tu, Z.; Tamura, Hajime*; Shirai, K.*; Kanekatsu, Rensuke*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Watanabe, Hiroshi
JAERI-Review 2000-024, TIARA Annual Report 1999, p.51 - 53, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Kiguchi, Kenji*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (85), p.30 - 36, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sakai, Takuro; Oikawa, Masakazu*; Sato, Takahiro*; Ishii, Keizo*; Sugimoto, Asuka*; Matsuyama, Shigeo*
International Journal of PIXE, 9(3&4), p.217 - 225, 1999/11
no abstracts in English
 ; Morphological changes of the nuclei and cells after spot irradiation
; Morphological changes of the nuclei and cells after spot irradiationKiguchi, Kenji*; Shima, T.*; Kinjo, Y.*; Tu, Z. L.*; Yamasaki, Shuhei*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Watanabe, Hiroshi
JAERI-Review 99-025, TIARA Annual Report 1998, p.53 - 55, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Watanabe, Hiroshi; Yamamoto, Kazuo
JAERI-Review 99-025, TIARA Annual Report 1998, p.50 - 52, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Tomihiro; Sakai, Takuro; *; Hirao, Toshio
Dai-11-Kai Tandemu Kasokuki Oyobi Sono Shuhen Gijutsu No Kenkyukai Hokokushu, p.126 - 128, 1999/01
no abstracts in English